AI Infrastructure Expansion Accelerates
The United States entered 2026 amid an unprecedented expansion of artificial intelligence infrastructure. Massive investments in data centers, advanced chips, and cloud platforms are rapidly reshaping the country’s industrial and technological landscape.
This buildout reflects the growing strategic importance of AI across economic productivity, national security, healthcare, and defense. Companies increasingly view scale, computing power, and data access as decisive competitive advantages that determine long-term market leadership.
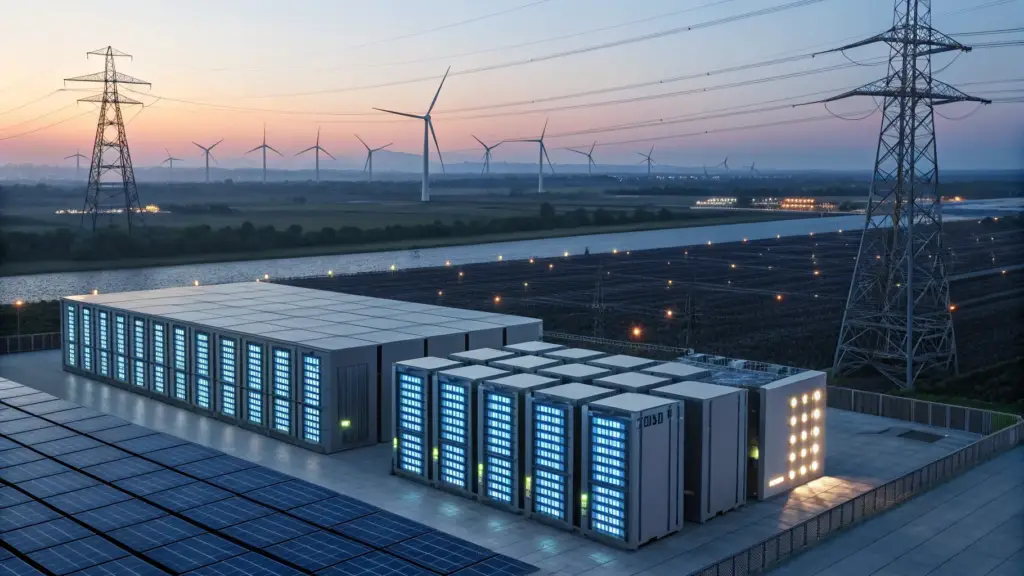

Data Centers Drive Surging Energy Demand
At the center of the AI boom are energy-intensive data centers that operate around the clock. Training and running large-scale AI models require enormous computing resources, pushing electricity consumption to record levels.
Utilities in several regions report mounting strain on existing power grids as new facilities come online. This surge has reignited debates over energy capacity, grid resilience, pricing stability, and the pace of infrastructure upgrades needed to support sustained growth.
Environmental Impact Comes Into Focus
The environmental footprint of AI infrastructure is drawing increased scrutiny from regulators and communities. While some firms invest heavily in renewable energy credits, on-site solar, and efficiency improvements, overall emissions linked to data center growth continue to rise.
Water usage for cooling has also emerged as a major concern, particularly in drought-prone regions. Local residents are questioning whether the economic benefits of AI infrastructure outweigh long-term environmental and resource costs.
Recommended Article: United States Accelerates AI Investment as Competition and Regulation Intensify
Regulatory Frameworks Lag Behind Innovation
Despite the speed of expansion, regulatory oversight of AI infrastructure remains fragmented and uneven. Zoning rules, environmental reviews, energy permits, and water-use approvals vary widely across states and municipalities.
Federal policymakers face growing pressure to establish clearer national standards. Industry leaders argue that predictable and streamlined regulation is essential to sustain investment while avoiding legal disputes and community opposition.
Big Tech Leads the Investment Wave
Major technology companies are driving the bulk of AI infrastructure spending in the United States. Their financial scale allows them to secure long-term power contracts, build proprietary chip architectures, and operate hyperscale data centers.
This concentration of infrastructure raises concerns about market dominance and access. Smaller firms, startups, and academic institutions may struggle to compete for computing resources as capacity becomes increasingly centralized.
Economic Benefits and Local Tensions
AI infrastructure projects deliver tangible economic benefits to host regions. Construction activity, permanent jobs, tax revenue, and supporting industries often make these projects attractive to local governments.
At the same time, residents express concerns over land use, rising electricity costs, noise pollution, and environmental strain. These tensions are shaping public opinion and influencing how future projects are evaluated and approved.
National Competitiveness at Stake
AI infrastructure has become a core element of national competitiveness and geopolitical strategy. US policymakers increasingly frame computing capacity as critical to maintaining technological leadership amid global competition.
This strategic lens complicates regulatory decisions. Balancing speed, sustainability, economic growth, and public trust remains a central challenge for both government and industry.
The Path Forward for US AI Growth
The AI infrastructure boom shows no signs of slowing as demand for advanced models and applications continues to rise. However, long-term viability will depend on careful management of energy systems, environmental impact, and regulatory clarity.
As 2026 unfolds, the United States faces a defining test: whether it can sustain AI leadership while protecting environmental stability, supporting local communities, and maintaining public confidence in technological progress.